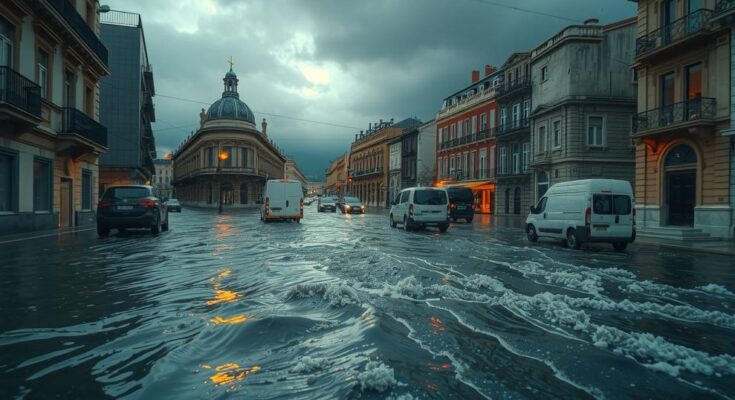
The NOAA-20 satellite captured images of a powerful storm over Spain on October 30, 2024, that delivered record rainfall leading to severe flooding. The storm’s effects were compounded by the inclusion of Saharan dust, resulting in widespread damage and emergency alerts in affected regions, particularly Valencia.
On October 30, 2024, the NOAA-20 satellite provided a notable image of a significant storm moving over Spain, characterized by unprecedented rainfall in the region. This image also illustrated the incorporation of Saharan dust from Africa into the storm.
The recent storm that ravaged eastern and southeastern Spain is a manifestation of extreme weather conditions exacerbated by global climate changes. The satellite imagery from NOAA-20 is essential for understanding the atmospheric dynamics involved, particularly the rare occurrence of Saharan dust combining with storm systems over Europe. The resultant heavy rainfall has led to devastation in various locales, underscoring the challenge posed by such natural disasters, which are becoming increasingly frequent in parts of the world due to climate instability.
In conclusion, the unprecedented storm that hit Spain on October 30, 2024, demonstrates the extreme weather events that contemporary meteorological agencies must contend with. The severe flooding has highlighted vulnerabilities within infrastructure in susceptible regions. The implications of such phenomena necessitate advanced monitoring systems, which are provided by satellites like NOAA-20, to enhance preparedness and response to future incidents.
Original Source: www.nesdis.noaa.gov